Artificial Cognition RSS
Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models
We explore how generating a chain of thought -- a series of intermediate reasoning steps -- significantly improves the ability of large language models to perform complex reasoning. In particular, we show how such reasoning abilities emerge naturally in sufficiently large language models via a simple method called chain of thought prompting, where a few chain of thought demonstrations are provided as exemplars in prompting. Experiments on three large language models show that chain of thought prompting improves performance on a range of arithmetic, commonsense, and symbolic reasoning tasks. The empirical gains can be striking. For instance, prompting a 540B-parameter...
Dissociating language and thought in large language models: a cognitive perspective
Today's large language models (LLMs) routinely generate coherent, grammatical and seemingly meaningful paragraphs of text. This achievement has led to speculation that these networks are -- or will soon become -- "thinking machines", capable of performing tasks that require abstract knowledge and reasoning. Here, we review the capabilities of LLMs by considering their performance on two different aspects of language use: 'formal linguistic competence', which includes knowledge of rules and patterns of a given language, and 'functional linguistic competence', a host of cognitive abilities required for language understanding and use in the real world. Drawing on evidence from cognitive neuroscience,...
What is Explainable AI?
Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) is a set of processes and methods that allows human users to comprehend and trust the results and output created by machine learning algorithms. Explainable AI is used to describe an AI model, its expected impact and potential biases. Sound complicated? Master Inventor Martin Keen gives you a simple (and fun) explanation on how explainable AI works.
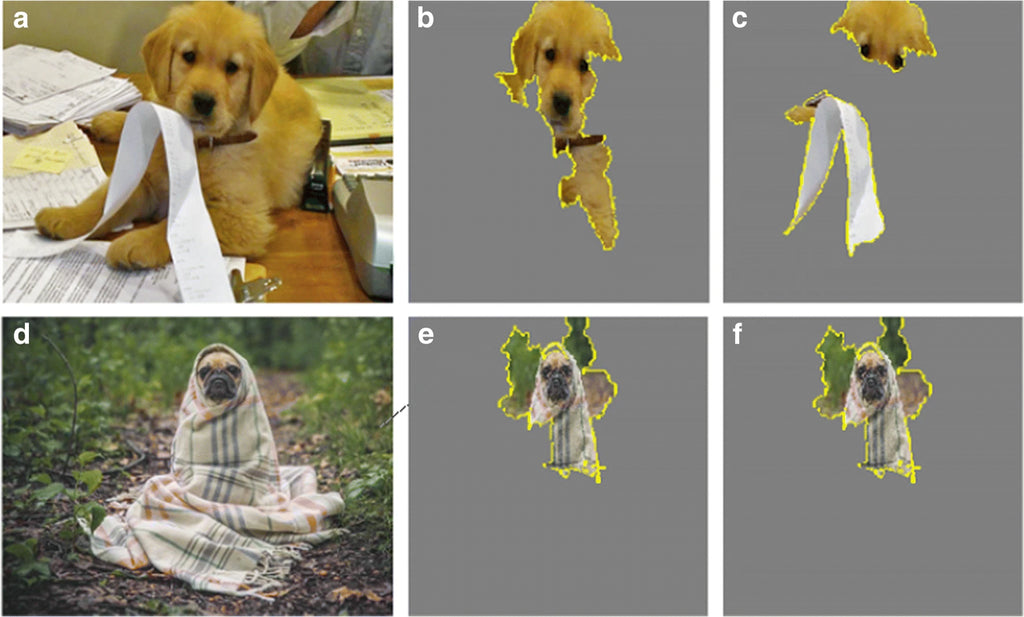
Artificial cognition: How experimental psychology can help generate explainable artificial intelligence
Abstract Artificial intelligence powered by deep neural networks has reached a level of complexity where it can be difficult or impossible to express how a model makes its decisions. This black-box problem is especially concerning when the model makes decisions with consequences for human well-being. In response, an emerging field called explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) aims to increase the interpretability, fairness, and transparency of machine learning. In this paper, we describe how cognitive psychologists can make contributions to XAI. The human mind is also a black box, and cognitive psychologists have over 150 years of experience modeling it through experimentation....
Theory of Mind Breakthrough: AI Consciousness & Disagreements at OpenAI [GPT 4 Tested]
What does the Theory of Mind breakthrough discovered in GPT 4 mean for the future of our interactions with language models? How might this complicate our ability to test for AI consciousness? I show the weaknesses of a range of tests of consciousness, and how GPT 4 passes them. I then show how tests like these, and other developments, have led to a difference of opinion at the top of OpenAI on the question of sentience. I bring numerous academic papers and David Chalmers, an eminent thinker on the hard problem of consciousness, and touch on ARC post yesterday on...
Tags
- All
- Agentic AI
- AGI
- AI
- AI Art
- AI Ethics
- AI Girlfriends
- AI Models
- AI Risk
- ai tools
- Alan D. Thompson
- Alexandr Wang
- Andrew Huberman
- Andrew Ng
- Artificial Cognition
- Aurora Supercomputer
- Authenticity
- Autism Spectrum
- AutoGPT
- Aza Raskin
- Azure Open AI
- Azure OpenAI Service
- Bias Compensation
- Bias Therapy
- Brian Roemmele
- Chain-of-Thought Prompting
- ChatGPT
- Christopher Rufo
- climate change
- Cognition Enhancement
- Cognitive Bias
- Cognitive Content
- Cognitive Performance
- Collective Intelligence
- Collective Stupidity
- Communication
- Consciousness
- Cosmology
- Critical Race Theory
- Daniel Dennett
- Daniel Schmachtenberger
- David Shapiro
- Deep Thought
- Dennis Prager
- Digital Minds
- Digital Thoughts
- Diversity
- Dojo
- Douglas Murray
- Elon Musk
- Emad Mostaque
- Equity
- Eric Weinstein
- Ethical Community Development
- Ethics
- Everyman
- Exponential Enterprise
- Fei-Fei Li
- Foresight
- Fred Lerdahl
- Frontiers Forum
- Futurecrafting
- Futurework
- Gary Marcus
- Gemini
- Gender
- Gender Pronouns
- Generative AI
- Generative Theory of Tonal Music (GTTM)
- Geoffrey Hinton
- Geoffrey Miller
- Glenn Loury
- Governance
- GPGICs
- GPT-4
- GPT-5
- Higher Education
- Human Potential
- Humanities
- Identity
- Ilya Sutskever
- Implicit Association Tests
- Intel
- Intelligence
- James Lindsay
- Joe Rogan
- Jordan B Peterson
- Jungian Archetypes
- Konstantin Kisin
- Language
- Lex Fridman
- Libra
- Life Coaching
- Liv Boeree
- Male Loneliness
- Marcus Aurelius
- Marcus T. Anthony
- Matt Walsh
- Matthew Berman
- Max Tegmark
- MemoryGPT
- Mental Health
- metabotropic receptors (MRs)
- Metacrisis
- Michio Kaku
- Microsoft AI
- Microsoft Copilot
- Microsoft Jarvis
- Microsoft Open AI
- Microsoft Semantic Kernel
- Millennials
- Mind Reading
- Minecraft
- Mirella Lapata
- MIT
- MLLM
- Moha Bensofia
- Morality
- Multimodal Large Language Model
- Multiversal Stories
- Music
- Narcissism
- Neurodivergence
- Neuroplasticity
- Neuroscience
- Nvidia
- OpenAI
- optical computers
- Personal Development
- Peter Bannon
- Peter H. Diamandis
- Philosophy
- pinecone
- Psychology
- Ramani Durvasula
- Ray Jackendoff
- Ray Kurzweil
- Reflection
- Reid Hoffman
- Relationships
- Religion
- Richard Haier
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- robotics
- Sabine Hossenfelder
- Sam Altman
- Sam Harris
- Sebastien Bubeck
- semantic search
- Seneca
- Simulation
- Singularity Ready
- Stephen Fry
- String theory
- Stupidity
- Super Alignment
- Superintelligence
- Susan Blackmore
- Synthetic Intelligence
- Synthetic Mind
- Technology
- Terence McKenna
- Tesla
- Tesla AI
- The Hero Archetype
- Theism
- Theory of Mind
- Thomas Sowell
- Thought
- Thought Experiments
- Transactivism
- transcendence
- Translation
- Tree of Thoughts
- Tristan Harris
- Turing Lectures
- Unconscious Bias Training
- Victor Davis Hanson
- Wes Roth
- Will Caster
- Woke Ideologies
- Worker Productivity
- Worker Satisfaction
- Yann LeCun
- Yuval Noah Harari




![Theory of Mind Breakthrough: AI Consciousness & Disagreements at OpenAI [GPT 4 Tested]](http://digitalhabitats.global/cdn/shop/articles/Theory_of_mind_may_have_spontaneously_emerged_from_LLM_1024x1024.png?v=1679250521)