The US Air Force is partnering with SpaceX to develop Starship for rapid Earth-to-Earth transportation and enhance military logistics, while also preparing for future lunar and Martian missions
Questions to inspire discussion
Starship Development Milestones
🚀 Q: What key capabilities must SpaceX perfect for Earth-to-Earth transportation?
A: SpaceX must master in-space engine relight, Mechazilla catch system landings, and re-entry with V2 upgrades including improved flaps and heat shields for extreme conditions.
🛬 Q: How many Starship landing pads is the US Air Force planning to build?
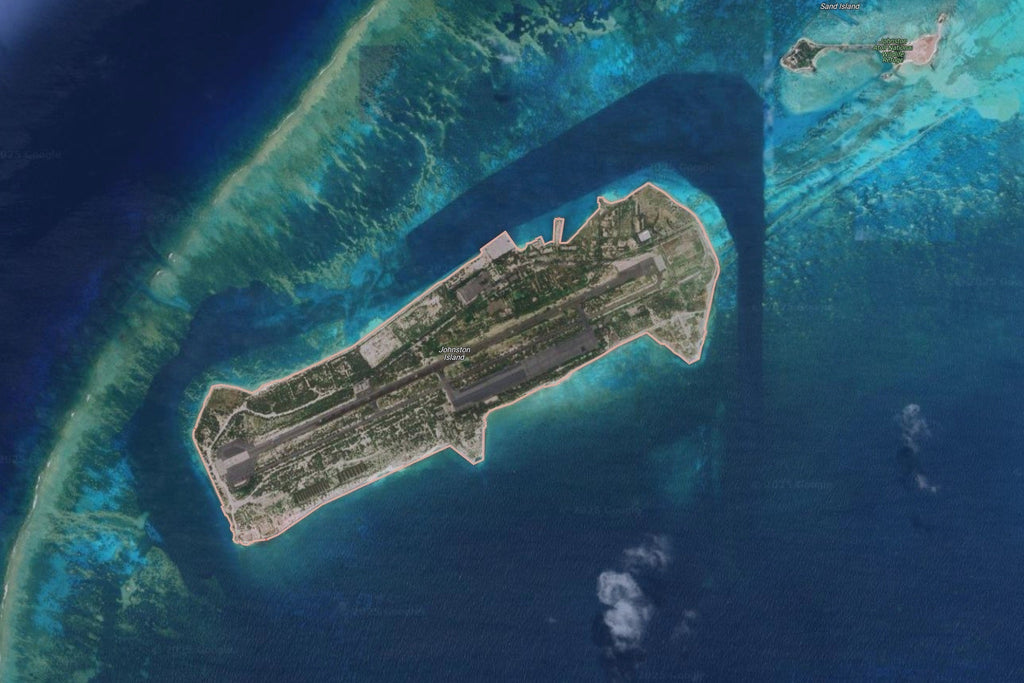
A: The USAF plans to construct two landing pads on Johnston Island, with potential for more in the future, emphasizing goals of high launch frequencies and seamless point-to-point transport.
Operational Projections
🚀 Q: What is SpaceX's projected launch rate for Starship?
A: SpaceX is aiming for a Starship launch rate of once a week within 12 months, with Starship V3 expected to achieve approximately 48 flights per year once operational.
Strategic Location
🗺️ Q: Why is Johnston Island an ideal location for Starship operations?
A: Johnston Island, located 700 nautical miles from Hawaii, serves as a strategic intermediate stop for routes between major continents and missions to remote regions like the Arctic and Antarctic.
Environmental Considerations
🌿 Q: What environmental steps are required before construction can begin?
A: The Pentagon must conduct an environmental impact study and release a detailed plan for public comment before construction can commence, potentially starting in May if approved.
Timeline
📅 Q: When could the Starship landing system on Johnston Island become operational?
A: If the plan receives support and approval, the system could be operational by early next year, following construction and testing phases.
Key Insights
Strategic Military Applications
🚀 The US Air Force plans to build two Starship landing pads on Johnston Island, a remote US territory 700 nautical miles from Hawaii, for Earth-to-Earth transportation capable of delivering cargo globally in 90 minutes or less.
🛰️ This initiative, led by the Air Force Research Laboratory, aims to support the development of commercial rocket technologies and achieve high launch frequencies for seamless point-to-point transport.
Technical Challenges
🔧 SpaceX must perfect in-space engine relight for Starship to adjust its trajectory after reaching orbit, a crucial capability for the Earth-to-Earth transportation concept.
🏗️ Mastering the Mechazilla catch system for landing Starship is essential, especially if a tower catching system is implemented for the landing pads.
Environmental and Logistical Considerations
🌿 The landing pads will be constructed within the Johnston Atoll National Wildlife Refuge, part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument, requiring an environmental impact study.
🗓️ If approved, construction could begin as early as May, with the system potentially operational by early next year, enabling rapid global deployment capabilities.
#SpaceX #StarportNetwork #MilitaryStarports
X Mentions: @SpaceX @USAIrForce
Clips
-
00:00 🚀 The US Air Force has unveiled a significant plan for SpaceX's Starship to facilitate rapid Earth-to-Earth transportation, signaling a new era for the technology.
-
01:05 🚀 The US Air Force plans to build two Starship landing pads on Johnston Island to enhance global transport capabilities, pending an environmental impact study and public feedback.
-
02:10 🚀 The US Air Force is building two landing pads for Starship missions to improve rapid cargo delivery for military and humanitarian operations.
- The US Air Force plans to construct two landing pads for Starship missions to support rapid cargo delivery worldwide, enhancing military and humanitarian operations.
- The new system could facilitate rapid response missions for global security, disaster relief, and emergency evacuations, benefiting both military and humanitarian efforts.
-
03:43 🚀 The US Air Force is collaborating with SpaceX to optimize Starship for upcoming moon and Mars missions, while the choice between landing legs and a robotic tower will influence future logistics.
- The US Air Force's initiative aims to enhance SpaceX's Starship for future moon and Mars missions through repeated launches and landings, supporting Artemis 3 in 2027 and long-term Mars plans.
- SpaceX must decide between using landing legs or a robotic tower system for Starship, which will impact future missions and construction logistics.
-
05:22 🚀 SpaceX must achieve reliable payload deployment and perfect in-space engine relight in upcoming flights to support the USAF's Earth-to-Earth mission plan.
-
06:38 🚀 SpaceX is focused on testing Starship's re-entry and landing for full reusability while aiming for weekly launches within a year.
- SpaceX needs to successfully test Starship's re-entry capabilities and landing techniques to achieve full reusability and maintain its competitive edge.
- SpaceX aims to increase its Starship launch frequency to once a week within a year, despite having only completed two V2 flights and still developing V2 prototypes.
-
08:15 🚀 SpaceX's Starship V3 is poised to revolutionize space travel with a target launch rate of once a week by 2026, significantly increasing its operational capacity.
-
09:39 🚀 Rocket Lab launched an Electron rocket on March 26, 2023, carrying eight wildfire detection satellites, achieving a rapid launch cadence with three missions in under two weeks.
- Rocket Lab successfully launched an Electron rocket on March 26, 2023, carrying eight wildfire detection satellites to enhance early detection and prevention of wildfires.
- Rocket Lab achieved an unprecedented rapid launch cadence with three missions in less than two weeks, marking its fifth mission of the year and the 63rd Electron launch overall.
-------------------------------------
Duration: 0:11:37
Publication Date: 2025-03-30T12:03:43Z
WatchUrl:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Eg5AZOrlhjQ
-------------------------------------